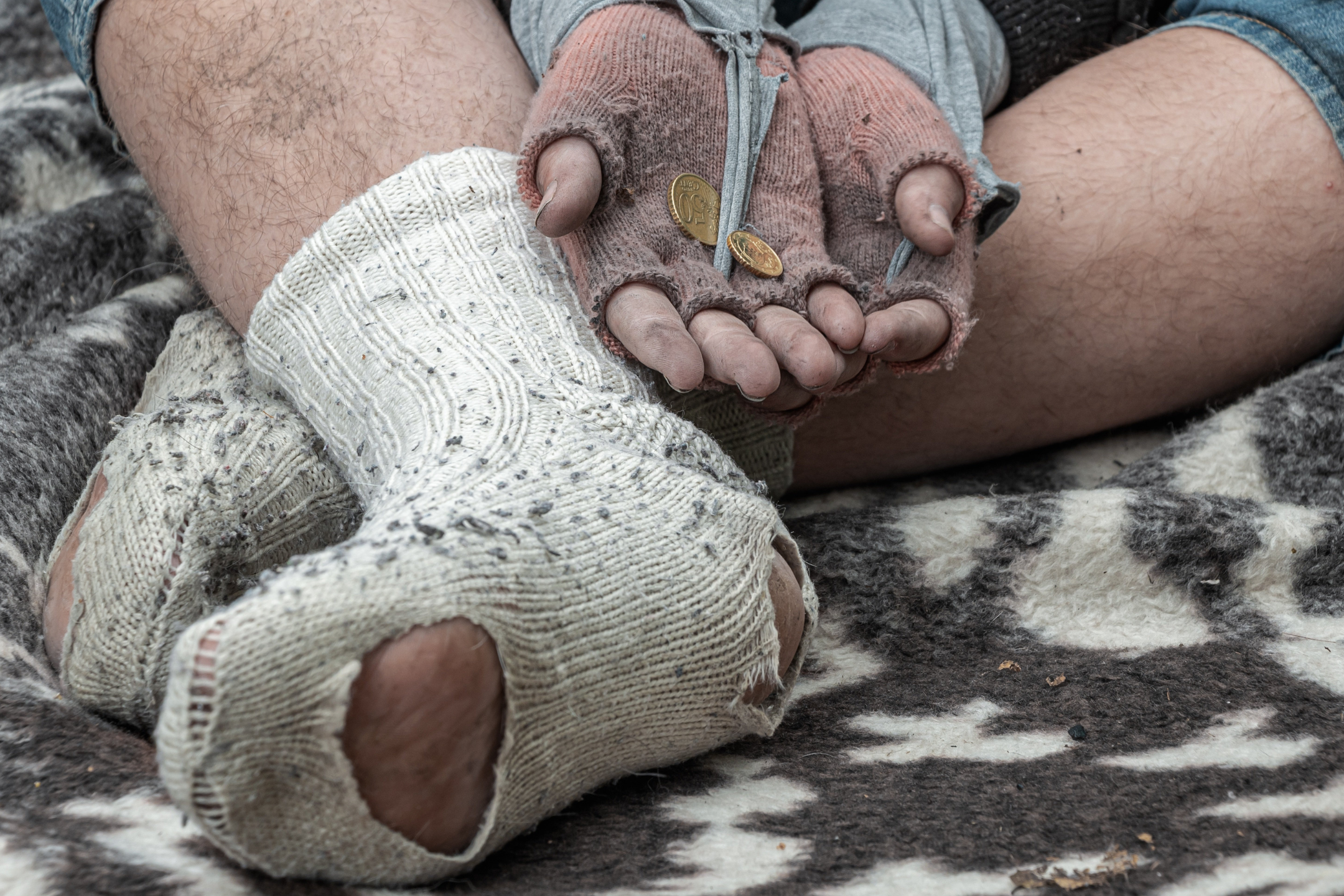
Human trafficking is one of the largest global crime industries. Let’s look into the reasons people become victims of trafficking, particularly how poverty and hunger play a role.
The Complexity of Human Trafficking
Human trafficking is a complex problem because it comes in many forms, happens worldwide, often goes unreported, targets vulnerable individuals, causes trauma, carries stigma, and is motivated by profit. It includes forced labor, sexual exploitation, and organ trafficking, making it hard to tackle. The criminals operate across borders, which makes it difficult for law enforcement to work together.
Victims usually belong to marginalized groups and find it hard to get help or talk about what happened to them. The suffering endured, paired with the money involved in trafficking, makes it even more challenging to fight this widespread and hidden crime.
What are Some of the Root Causes of Human Trafficking
The root causes of human trafficking are often stemming from a combination of social, economic, and political factors. Some common root causes include:
1. Poverty: Economic inequality and lack of opportunities can push individuals into vulnerable situations where they are more susceptible to trafficking. The poor are subsequently preyed upon by manipulative traffickers offering false promises of employment and education opportunities, remuneration in addition to a better life condition.
2. Lack of Education: Limited access to education, especially for marginalized communities, can contribute to a lack of awareness and vulnerability to trafficking schemes.
3. Conflict and Instability: Wars, conflicts, and political instability can displace populations and create environments where trafficking thrives.
4. Gender Inequality: Discrimination against women and girls, as well as societal norms that devalue their worth, can make them more susceptible to exploitation and trafficking.
5. Lack of Law Enforcement: Weak law enforcement, corruption, and lack of enforcement of anti-trafficking laws can allow traffickers to operate with impunity.
6. Demand for Cheap Labor and Services: The demand for cheap labor, commercial sex, and exploitative services fuels the supply side of human trafficking.
7. Globalization: The interconnected nature of the global economy can facilitate the movement of people across borders, making it easier for traffickers to exploit individuals.
Poverty as One of the Primary Causes of Human Trafficking & Its Relation with Hunger
Poverty is considered one of the primary causes of human trafficking. Hunger and poverty are interconnected issues, with hunger often stemming from poverty or exacerbating it further. Individuals facing extreme poverty and lack of access to basic necessities like food become more vulnerable to exploitation, including human trafficking. Addressing poverty and its associated factors is crucial in combating human trafficking and improving the overall well-being of individuals and communities.

UN Organizations that Recognize Poverty & Hunger as One of the Root Causes for Human Trafficking
Several United Nations (UN) organizations recognize poverty and hunger as significant root causes for human trafficking. Some of these UN organizations include:
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC): UNODC recognizes poverty and lack of economic opportunities as key to human trafficking. The organization works to combat trafficking through various initiatives, including raising awareness, capacity-building, and supporting the implementation of legal frameworks to address trafficking.
- International Labour Organization (ILO): The ILO highlights the link between poverty, lack of decent work opportunities, and vulnerability to exploitation, including human trafficking for forced labor. The organization promotes decent work and advocates for fair labor practices to help prevent labor exploitation.
- United Nations Development Programme (UNDP): UNDP acknowledges the connection between poverty, social inequality, and human trafficking. The organization focuses on promoting sustainable development, poverty reduction, and economic empowerment as part of efforts to prevent trafficking and support victims.
- United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF): UNICEF recognizes that children living in poverty are at higher risk of being trafficked for purposes such as forced labor, sexual exploitation, or recruitment into armed groups. The organization works to protect children from exploitation and supports interventions that address poverty and social disparities.
- World Food Programme (WFP): WFP addresses the intersection of hunger and human trafficking by providing food assistance to vulnerable populations, including those at risk of being trafficked. By addressing food insecurity, WFP aims to reduce vulnerabilities that can lead to exploitation.
These organizations, among others within the UN system, emphasize the importance of addressing poverty, hunger, and social inequalities to prevent human trafficking and protect individuals from exploitation.

Strategies to Alleviate Poverty & Hunger to Minimize Human Trafficking World Wide
UN organizations target the root causes of poverty and hunger to prevent human trafficking through a variety of strategies. They implement poverty alleviation programs that focus on creating job opportunities, vocational training, and income-generating activities to improve economic conditions and reduce vulnerability to trafficking.
Education initiatives are promoted to provide access to quality education, empowering individuals with knowledge and skills to make informed choices and avoid situations that may lead to trafficking. Social protection schemes are advocated for and implemented to provide assistance to those living in poverty, including cash transfers, food assistance, and healthcare services to address basic needs and improve well-being.
UN organizations work with governments to develop and strengthen legal and policy frameworks that combat poverty, hunger, and human trafficking. They also conduct capacity-building initiatives and awareness campaigns to enhance the capabilities of local communities, governments, and organizations in preventing trafficking.
Community empowerment is emphasized through community-based approaches, enabling communities to identify and address factors contributing to poverty and hunger. Collaboration and partnerships with various stakeholders are facilitated to address complex issues through leveraging expertise, resources, and networks for more effective prevention strategies.
By addressing these root causes through multifaceted approaches, UN organizations aim to create environments where individuals are less susceptible to exploitation and trafficking.